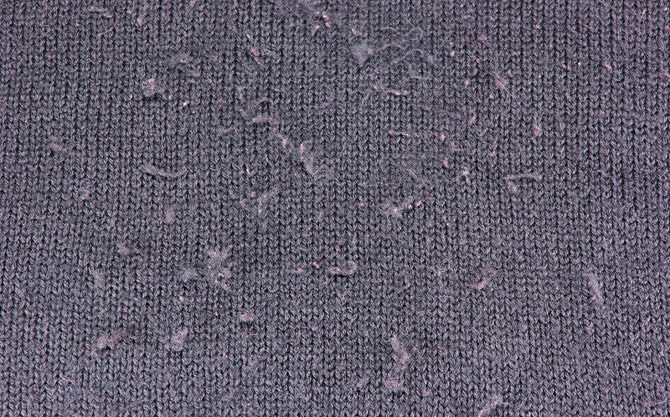
UNWANTED EFFECT – PILLING
Pilling is an undesired effect in textiles, consisting of the formation of pills or lint balls on the surface of the fabric due to tangled fibers. This causes aspects of aging or prolonged use in very short periods of time. Consequently, pilling is an undesirable effect to be avoided, so it must be anticipated from the initial design of the fabric, through the proper choice of fibers, thread structure, and final finishing operations.
In the research and development department, in conjunction with the quality department, we closely study the phenomenon of pilling and develop strategies to prevent its formation. We conduct numerous tests both at the beginning of fabric construction and on the finished fabric.
To prevent or minimize pilling, a deep understanding of the fibers to be used, as well as the structure of the yarns and fabric in question, is necessary.
The following aspects should be taken into account:
Parameters affecting the fiber.
Parameters affecting the yarn.
Parameters affecting the fabric.
Parameters affecting dyeing and finishing.
FIBERS
We will review the main parameters of fibers and how these affect the formation of pilling.
– Fiber Nature:
Synthetic fibers have a higher tendency to form pilling than natural fibers. This is due to their higher strength and flexibility.
– Fiber Fineness:
The finer the fiber (lower Dtex), the greater the propensity for pilling in the yarn, as it will have a greater ease of migration to the surface of the yarn.
– Fiber Curliness:
Smooth cross-sectional profiles facilitate the migration of fibers to the exterior of the yarns and, consequently, contribute to pilling.
– Fiber Length:
Shorter fiber length increases the propensity for pilling, as it has greater ease of migration to the surface of the yarn and, consequently, the fabric.
Dabedan pays close attention during the spinning process, aiming to avoid breaking fibers, especially during the carding operation. Breaking fibers results in a shorter length distribution, which can contribute to increased pilling.
YARNS
The yarn structure also has a significant influence on the propensity for pilling in textiles finished with them.
Let’s now examine the most important parameters and how they influence the generation of pilling.
– Yarn Count:
The higher the yarn count (thicker yarn), the greater the number of fibers per cross-section, and therefore, a higher propensity for pilling.
– Yarn Twist and Ply Twist:
Higher yarn twist results in less pilling formation, as the fibers will be more tightly bound, making it more difficult for them to migrate to the surface.
– Finishes Applied to the Yarn:
A yarn that has been singed to remove surface fuzz will have a lower propensity for pilling.
– Blend of Fibers of Different Lengths:
In a blend of long and short fibers, the short fibers tend to migrate to the surface of the yarn, giving the appearance of excessive surface fuzz.
– Blend of Different Materials:
When blending fibers of different fineness and length, the finer ones will remain on the interior, while the thicker and shorter ones will migrate to the exterior.
In general, for open-weave fabrics, it can be said that:
Longer floats in the fabric generally result in greater pilling formation
Higher weave density generally leads to lower pilling formation
Higher fabric density percentage or greater weight generally correlates with lower tendency to form pilling
FABRIC PREPARATION OPERATIONS:
To minimize pilling formation, Dabedan subjects its fabrics to a series of preparatory pre-treatments:
– Brushing:
It aims to remove fibers and prepare the surface for subsequent treatments
– Singeing:
ingeing removes surface fuzz from the fabric through burning or charring It is preceded by brushing as a preparatory operation
– Shearing:
It aims to cut the surface fibers of the fabric (fuzz) It also involves brushing as a preparatory operation.
DYEING AND FINISHING OPERATIONS ON FABRICS:
In the final finishing processes, Dabedan subjects its fabrics to dyeing, sizing, and finishing operations, which are directly related to the potential future formation of pilling.
– Scouring and Desizing:
The complete removal of waxes and lubricants from fibers and yarns will reduce the propensity for pilling, as there are no substances that promote it.
– Heat Setting:
Both steaming and heat setting reduce the tendency for pilling by ‘setting’ the fibers in a specific position, preventing their easy migration to the external areas of the fabric.
It is crucial to control the optimal heat-setting temperature for each type of fiber.
– Softening:
Softeners decrease the coefficient of friction between fibers, thereby reducing their tendency to pilling.
– Sizing and Anti-Pilling Agents:
These sizing products, in the form of resins, act as binding or fixing elements for the fibers.
As observed, the number of variables influencing pilling formation is substantial. Furthermore, considering the interaction of various parameters adds complexity to the study of pilling.
At Dabedan, with over 40 years of experience, we anticipate this phenomenon from the conception and design stage of the fabric.
For us, the combination of technical, technological, and design knowledge is fundamental.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Receive all communications in your email to stay up to date with our news, as well as news and advice about the sector.
Latest published articles
Do you need advice?
We collaborate with you to develop custom designs tailored to the needs of each project, creating the fabric according to aesthetic, quality, or usage requirements.
Get in touch with us, and we will advise you on our products, or request a free sample.


